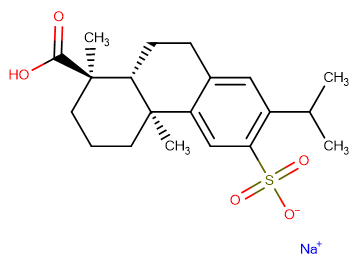
Ecabet Sodium
CAS No. 86408-72-2
Ecabet Sodium( —— )
Catalog No. M16263 CAS No. 86408-72-2
Ecabet sodium: a potential new agent in the management of distal colitis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 39 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 87 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 129 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 188 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEcabet Sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEcabet sodium: a potential new agent in the management of distal colitis.
-
DescriptionEcabet sodium: a potential new agent in the management of distal colitis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number86408-72-2
-
Formula Weight402.48
-
Molecular FormulaC20H27NaO5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESCC(C)C1=C(C=C2C(=C1)CC[C@@H]3[C@@]2(CCC[C@@]3(C)C(=O)O)C)S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Lawrance IC. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jul;25(7):1182-4.
molnova catalog



related products
-
[Des-Leu9]-Kinetensi...
[Des-Leu9]-Kinetensin
-
Pallidol
Pallidol is a potent and selective singlet oxygen quencher in aqueous systems, it may be used in singlet oxygen-mediated diseases as a pharmacological agent.
-
Ingenol-5,20-acetoni...
Ingenol-5,20-acetonide-3-O-angelate is a natural product.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


